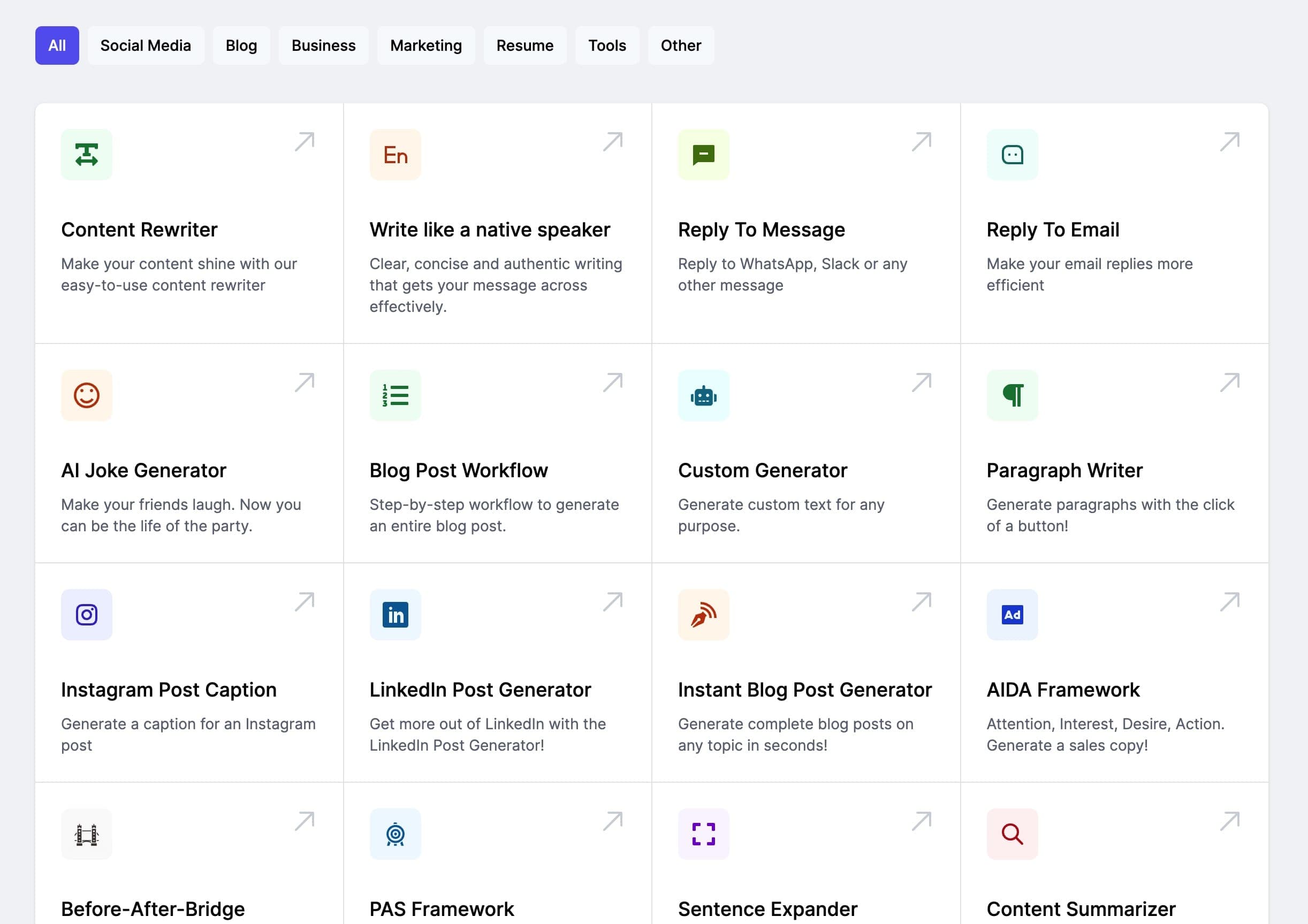
Case History Age: 12;0 Sex: Female Presenting problem: Fluctuating hearing & Constant ear drainage resulting in strong pungent odour near her ears Past Medical History: Chronic otitis media & Bilateral mastoidectomies Present Medical Management: Family doctor dismissing possibility of improvement in hearing & Currently on renewable eardrops prescription Family History: No family history of hearing loss Use of Hearing Aid History: Has had hearing aid on right ear, but unusable due to constant ear drainage
Clinical Summary Update
1. Client Overview and Current Treatment Context
The client is a 12-year-old female presenting with fluctuating hearing and persistent ear drainage, accompanied by a strong pungent odor near her ears. She has a medical history significant for chronic otitis media (COM) and has undergone bilateral mastoidectomies. Currently, her family doctor has dismissed the possibility of improvement in her hearing, while she remains on a renewable eardrops prescription to manage her ear condition. Despite having previously used a hearing aid in her right ear, it is now rendered unusable due to the continuous ear drainage.
2. Recent Observations and Changes in Symptoms
Recent clinical observations indicate that the client continues to experience ongoing ear drainage, which is consistent with her history of COM. The drainage appears to have a strong odor, suggesting potential infection or complications within the middle ear that require further medical intervention. No significant improvements in hearing have been noted since her last assessment, indicating the need for a more aggressive approach to her treatment plan.
3. Progress Toward Treatment Goals
The client has engaged in aural rehabilitation activities, including auditory and compensatory training. However, progress has been limited due to the persistent ear drainage and fluctuating hearing levels. Key treatment goals—such as improving auditory comprehension and developing effective communication strategies—have been hindered. The client has shown some ability to anticipate scenarios and practice selective attention, yet challenges remain due to her fluctuating auditory status and communication breakdowns during interactions.
4. Updates to the Treatment Plan
To address the client’s ongoing issues, the following updates to the treatment plan are recommended:
Medical Intervention: A referral to an ENT specialist is deemed critical to evaluate the persistent ear drainage and assess the need for surgical options, such as tympanoplasty, to reconstruct the tympanic membrane. Aggressive medical management is necessary to manage her chronic otitis media effectively.
Hearing Aid Management: The use of a Behind-the-Ear (BTE) hearing aid fitted with non-occluding earmolds is recommended, with daily maintenance checks and cleaning protocols to ensure optimal functioning, pending medical clearance.
Auditory and Compensatory Training:
Anticipatory Strategy Training: Continue to use visual and auditory methods to help the client anticipate interactions within classroom settings.
Selective Attention Training: Implement auditory activities focusing on voice discrimination to enhance the client’s ability to filter competing sounds.
Repair Strategy Training: Teach the client the specific communication repair strategies to manage breakdowns during conversations effectively.
Auditory Comprehension Training: Focus on enhancing the client’s ability to comprehend key story elements, crucial for academic success.
School-Based Support: Develop an Individualized Education Plan (IEP) to outline specific goals and accommodations that cater to the client’s auditory needs and support her academic progress.
Caregiver and Communication Partner Training: Engage caregivers and communication partners, including teachers and peers, in strategies to create a supportive communication environment that reduces background noise and reinforces effective listening strategies.
5. Justification for Continued Treatment and/or Insurance Authorization
Given the client’s complex medical history, including chronic otitis media and its associated complications, continued treatment is medically necessary to manage her auditory health and overall quality of life. The mixed-type hearing loss, evidenced by audiometric tests, necessitates a multi-faceted approach that includes medical intervention, auditory training, and educational support. The proposed treatment plan aims to prevent further infection, enhance auditory-cognitive skills, and facilitate smoother communication in school environments. Therefore, insurance authorization for continued treatment and the proposed interventions is justified based on the client’s medical necessity and the potential for significant improvement in her hearing and communication abilities.
In summary, the ongoing challenges posed by the client’s fluctuating hearing and ear drainage require immediate medical assessment and a tailored rehabilitation approach to support her educational and social interactions effectively.