Table of Contents
- Introduction to Bot Actions
- Why Actions Matter: From Knowledge to Agency
- The 8 Bot Actions Explained
- Setting Up Your First Action
- Best Practices
- Real-World Use Cases
- Combining Multiple Actions
- Troubleshooting
- FAQs
Introduction to Bot Actions
Bot Actions transform your chatbot from a simple question-answering system into an intelligent agent that can execute real tasks. Instead of just retrieving information from a knowledge base, your bot can:
- Call external APIs to fetch real-time data
- Generate and display forms to collect structured information
- Send emails to your team or customers
- Schedule calendar events automatically
- Search the web for current information
- Execute Python code for calculations and data analysis
- Scrape websites for dynamic content
- Create interactive buttons for quick user actions
Think of Actions as giving your chatbot “hands and feet” to interact with the real world, not just a “mouth” to answer questions.
Why Actions Matter: From Knowledge to Agency
The Evolution of Chatbots
Traditional Chatbots (Knowledge-Based)
- Limited to pre-uploaded information
- Can only answer questions about what they “know”
- Passive: user asks → bot responds
- Static data that becomes outdated
- No integration with external systems
Agentic Chatbots (Action-Based)
- Access real-time information from any source
- Can perform tasks and complete workflows
- Proactive: anticipates needs and suggests actions
- Always current with live data connections
- Seamlessly integrated with your tech stack
Real-World Impact
Example: E-commerce Store
Without Actions:
- User: “Do you have blue hoodies in stock?”
- Bot: “According to our last update in October, we had 15 blue hoodies.”
- Problem: Information might be outdated
With Actions:
- User: “Do you have blue hoodies in stock?”
- Bot: [Calls inventory API] “Yes! We currently have 23 blue hoodies available in sizes S-XL. Would you like to see them?”
- Solution: Real-time, accurate information
The 8 Bot Actions Explained
1. Custom Action
What it does: Connects your bot to any external API, database, or custom system. This is the most powerful and flexible action type.
When to use it:
- Fetching real-time data from your systems (inventory, pricing, user accounts)
- Integrating with third-party APIs (Stripe, Shopify, Salesforce)
- Triggering custom workflows in your backend
- Executing proprietary business logic
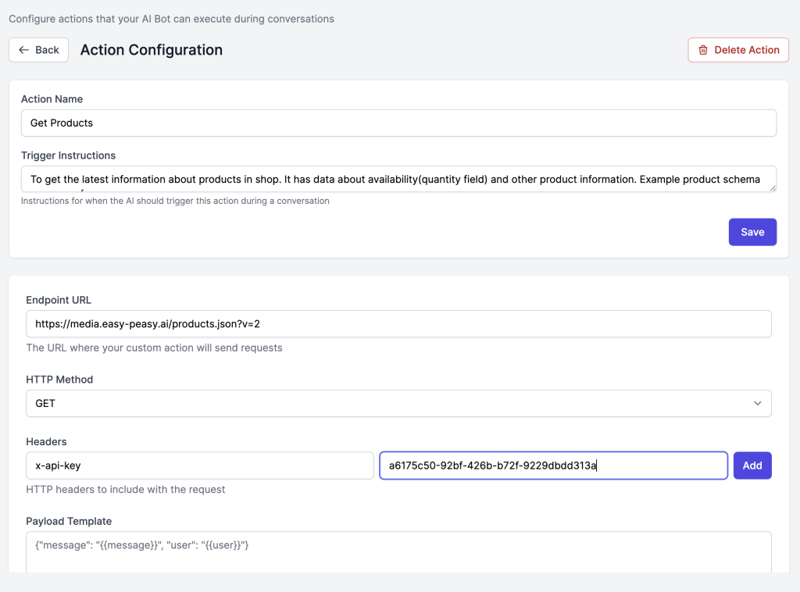
Configuration:
Name: Get Product Inventory
Description: Fetches current product availability and details
Trigger Condition: When user asks about product availability or stock
API Endpoint: example.com/api
Method: GET
Headers:
- Authorization: Bearer YOUR_API_KEY
- Content-Type: application/json
Query Parameters:
- products: all
- include_availability: true
Use Cases:
- E-commerce: Check inventory, fetch product details, verify pricing
- SaaS: Query user account status, subscription details, usage limits
- Healthcare: Check appointment availability, retrieve patient records (HIPAA-compliant)
- Real Estate: Get property listings, check availability, calculate mortgage estimates
- Banking: Check account balance, recent transactions, fraud alerts
Best Practices:
- ✅ Use clear, descriptive trigger conditions
- ✅ Implement proper authentication and API key management
- ✅ Handle errors gracefully with fallback responses
- ✅ Test with various input scenarios
Example Response Handling:
The bot receives:
{
"product": "Premium Hoodie",
"price": 75.00,
"currency": "USD",
"quantity": 23,
"image": "https://..."
}
Bot can respond: “Great news! The Premium Hoodie is in stock with 23 units available at $75.00. Here’s what it looks like: [image]”
2. Custom Button
What it does: Creates interactive buttons within the chat interface that users can click for quick actions.
When to use it:
- Providing quick action options to users
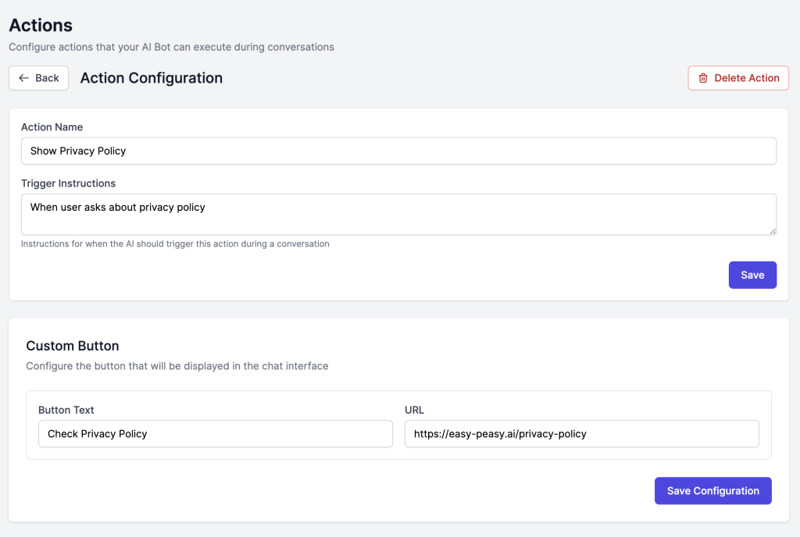
Configuration:
Name: Show Privacy Policy
Trigger Condition: When user asks about privacy policy
Button Text: Check Privacy Policy
URL: https://easy-peasy.ai/privacy-policy
Use Cases:
- Customer Support: Category selection, issue types, escalation options
- Booking Systems: Date selection, time slots, service types
- Surveys: Quick feedback, rating buttons, yes/no questions
- Navigation: Menu options, category browsing, feature discovery
- Onboarding: Step-by-step guided tours, tutorial progression
Best Practices:
- ✅ Use clear, action-oriented labels (“Track Order” not “Tracking”)
3. Custom Form
What it does: Generates and displays interactive forms to collect structured information from users.
When to use it:
- Collecting multiple pieces of information at once
- Lead generation and qualification
- Order forms, registration, surveys
- Structured data entry (better than back-and-forth questions)
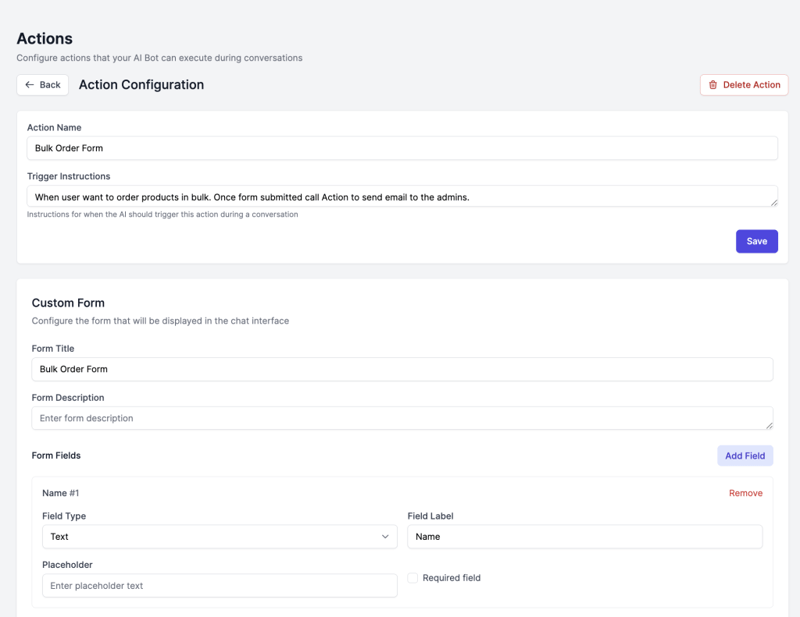
Configuration:
Name: Bulk Order Form
Description: Collect bulk order requests from businesses
Trigger Condition: When user wants to order products in bulk or mentions large quantities
Fields:
Field 1:
- ID: name
- Type: text
- Label: Full Name
- Required: Yes
- Placeholder: John Doe
Field 2:
- ID: email
- Type: email
- Label: Email Address
- Required: Yes
- Validation: email
Field 3:
- ID: company
- Type: text
- Label: Company Name
- Required: No
Field 4:
- ID: product
- Type: select
- Label: Product
- Required: Yes
- Options: Premium Hoodie, Men’s T-Shirt, Women’s T-Shirt, Tote Bag
Field 5:
- ID: quantity
- Type: number
- Label: Quantity
- Required: Yes
Field 6:
- ID: notes
- Type: textarea
- Label: Special Requirements
- Required: No
- Placeholder: Any custom printing, colors, or special requests?
Use Cases:
- Lead Generation: Contact forms, demo requests, pricing inquiries
- E-commerce: Bulk orders, custom product requests, quote requests
- Support: Detailed issue reports, feedback collection, bug reports
- Booking: Appointment scheduling, reservation details, event registration
- HR: Job applications, employee onboarding, time-off requests
Best Practices:
- ✅ Only ask for essential information (reduce friction)
- ✅ Use appropriate field types for validation
- ✅ Provide helpful placeholder text and labels
- ✅ Mark required vs. optional fields clearly
Form Submission Handling:
When a user submits the form, you can:
- Store in leads database (automatically captured in Easy-Peasy.AI)
- Trigger email notifications (to admins or user)
- Call custom API to process in your system
- Update CRM (via Zapier or direct integration)
4. Fetch URL
What it does: Retrieves content from any publicly accessible URL during conversations. Think of it as giving your bot a web browser.
When to use it:
- Pulling content from specific web pages
- Monitoring competitor websites
- Checking product availability on external sites
- Retrieving documentation or help articles
- Accessing public APIs without custom configuration
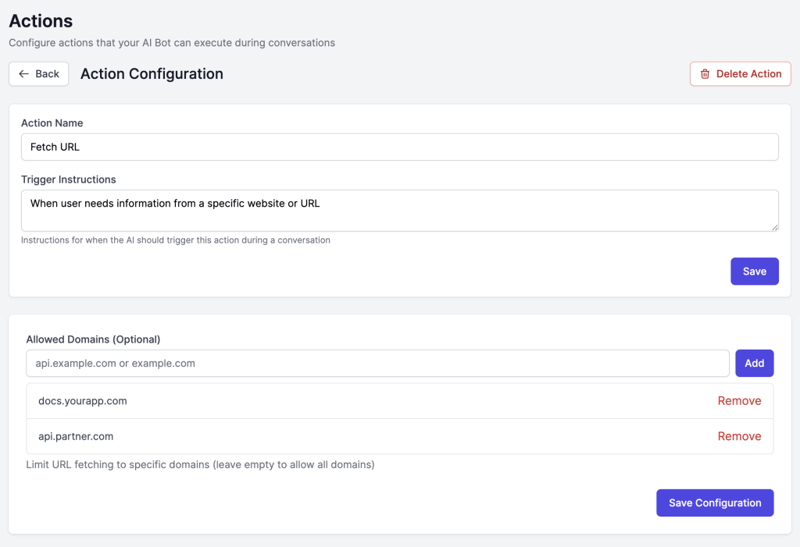
Configuration:
Name: Fetch URL Content
Description: Retrieve information from external websites
Trigger Condition: When user needs information from a specific website or URL
Allowed Domains:
- example.com
- docs.yourapp.com
- api.partner.com
Use Cases:
- Competitor Monitoring: Check competitor pricing, features, availability
- Content Aggregation: Pull news, blog posts, documentation
- Verification: Confirm information from authoritative sources
- Integration: Access public APIs without custom action setup
- Research: Gather information from multiple sources
Example Conversation:
User: “What’s the current price of Bitcoin?”
Bot: [Fetches URL: https://api.coinbase.com/v2/prices/BTC-USD/spot]
Bot: “The current Bitcoin price is $43,250 USD according to Coinbase.”
Best Practices:
- ✅ Whitelist trusted domains for security
Limitations:
- Cannot access password-protected content
- May not work with JavaScript-heavy SPAs
- Subject to rate limiting and blocking
- No way to interact with forms or buttons on fetched pages
5. Code Interpreter
What it does: Executes Python code in a secure sandbox environment. Your bot can perform calculations, analyze data, generate charts, process files, and solve complex problems.
When to use it:
- Complex calculations and math problems
- Data analysis and visualization
- File processing (CSV, Excel, JSON)
- Statistical analysis
- Scientific computations
- Chart and graph generation
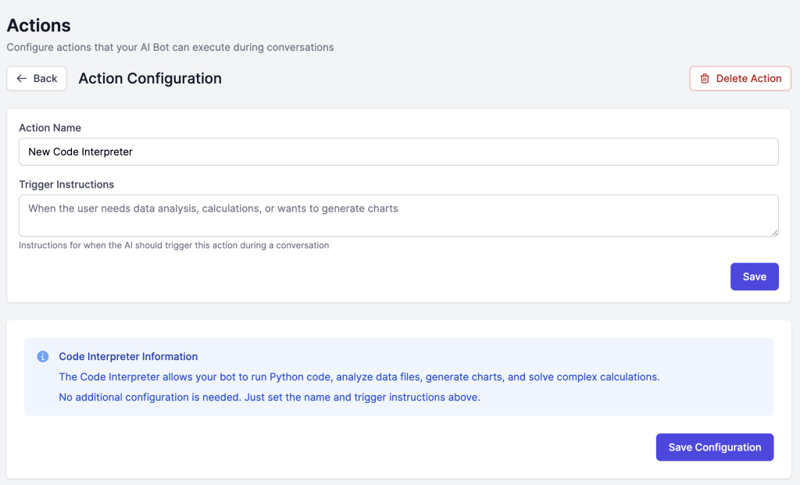
Configuration:
Name: Code Interpreter
Description: Run Python code for calculations, data analysis, and visualizations
Trigger Condition: When user needs calculations, data analysis, charts, or complex problem-solving
Use Cases:
- Finance: Calculate ROI, loan payments, investment returns, financial modeling
- Analytics: Process datasets, generate reports, statistical analysis
- Education: Solve math problems, explain step-by-step solutions
- Engineering: Unit conversions, physics calculations, simulations
- Business Intelligence: Sales forecasts, trend analysis, KPI calculations
- Data Visualization: Create custom charts, graphs, heatmaps
Example Conversations:
Example 1: Financial Calculation
- User: “If I invest $10,000 at 7% annual return compounded monthly for 10 years, what will I have?”
- Bot: [Executes Python calculation]
- Bot: “With monthly compounding at 7% annual interest, your $10,000 investment would grow to approximately $20,096.61 after 10 years.”
Example 2: Data Analysis
- User: “Can you analyze this sales CSV and show me which product sold best?”
- Bot: [Processes uploaded file, generates chart]
- Bot: “Based on your data, Premium Hoodies generated the highest revenue at $45,230, followed by T-Shirts at $38,450. Here’s a visualization: [chart image]”
Best Practices:
- ✅ Clearly explain what code will be executed
Security:
All code runs in an isolated sandbox with:
- No access to your servers or databases
- Limited memory and CPU
- Restricted network access
- No persistent storage between executions
6. Web Search
What it does: Performs real-time Google searches to find current information, news, and answers to questions beyond your bot’s knowledge base.
When to use it:
- Answering questions about current events
- Finding up-to-date information (news, weather, stock prices)
- Researching topics beyond your knowledge base
- Fact-checking and verification
- Product research and comparisons
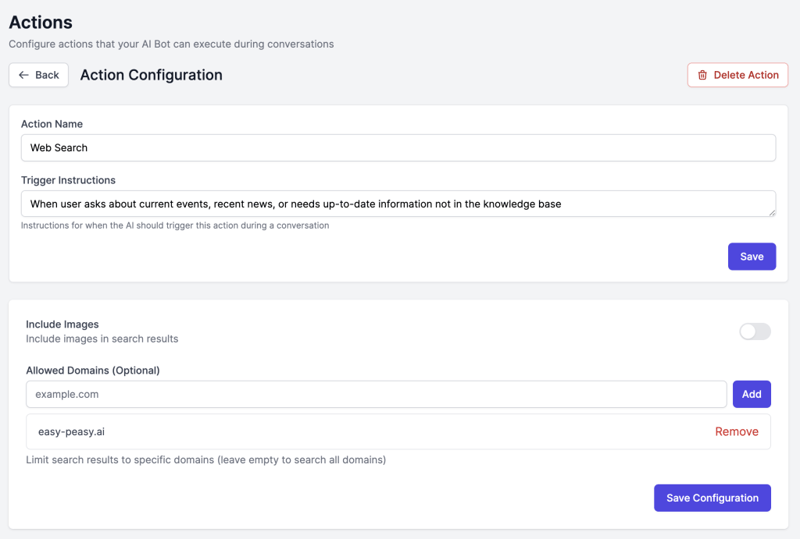
Configuration:
Name: Web Search
Description: Search the web for current information and real-time data
Trigger Condition: When user asks about current events, recent news, or needs up-to-date information not in the knowledge base
What Gets Searched:
- Recent news articles
- Web pages and blogs
- Wikipedia and knowledge bases
- Product listings and reviews
- Social media (public posts)
- Government and official sources
Use Cases:
- News & Current Events: “What’s happening with AI regulation in the EU?”
- Weather: “What’s the weather like in Singapore this week?”
- Stock Prices: “What’s Tesla’s current stock price?”
- Product Research: “What are the best budget laptops in 2025?”
- Fact-Checking: “Did SpaceX launch a rocket yesterday?”
- Competitive Intelligence: “What new features did Competitor X announce?”
- Travel Information: “Are flights to Japan running normally?”
Example Conversations:
Example 1: Current Events
- User: “What’s the latest news about ChatGPT?”
- Bot: [Performs web search]
- Bot: “According to recent sources, OpenAI released GPT-5 in August 2025 with improved reasoning capabilities. Here are the key updates: [summary from search results with sources]”
Example 2: Real-Time Data
- User: “What’s the current exchange rate for USD to EUR?”
- Bot: [Searches for current rates]
- Bot: “As of today, 1 USD = 0.92 EUR (source: xe.com)”
Best Practices:
- ✅ Always cite sources for information
- ✅ Include publication dates for time-sensitive info
- ✅ Combine multiple sources for accuracy
- ✅ Use safe search to filter inappropriate content
Limitations:
- Results may include outdated cached pages
- Cannot access paywalled content
- Limited to publicly available information
- Subject to search engine biases and SEO manipulation
- May return irrelevant results for ambiguous queries
7. Email Notification
What it does: Sends automated email notifications based on user interactions and bot events.
When to use it:
- Notifying your team of important events (leads, support tickets, orders)
- Sending confirmation emails to users
- Escalating issues to human agents
- Delivering receipts, reports, or documents
- Follow-up communications
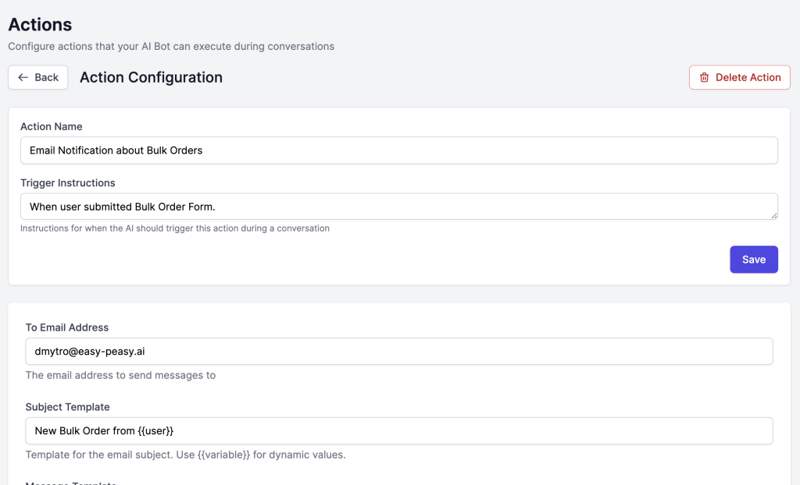
Configuration:
Name: Bulk Order Alert
Description: Send email to sales team when bulk order form is submitted
Trigger Condition: When user submits the bulk order form
Email Settings:
To: [email protected], [email protected]
Subject: 🛍️ New Bulk Order Request – {{user}}
Use Cases:
1. Lead Notifications
- New lead captured → Email to sales team
- Demo request → Email to account executive
- Contact form → Email to support
2. Order Management
- Order placed → Confirmation to customer + notification to fulfillment
- Order shipped → Tracking info to customer
- Order issue → Alert to support team
3. Support Escalation
- Negative sentiment detected → Email to supervisor
- High-priority issue → Immediate notification
- Unresolved after 3 messages → Human handoff
4. Form Submissions
- Bulk order request → Sales team
- Partnership inquiry → Business development
- Bug report → Engineering team
Best Practices:
- ✅ Use clear, descriptive subject lines
8. Google Calendar
What it does: Creates, updates, and manages Google Calendar events directly from chat conversations.
When to use it:
- Scheduling appointments and meetings
- Booking consultations or demos
- Setting reminders for follow-ups
- Managing team calendars
- Coordinating events with customers
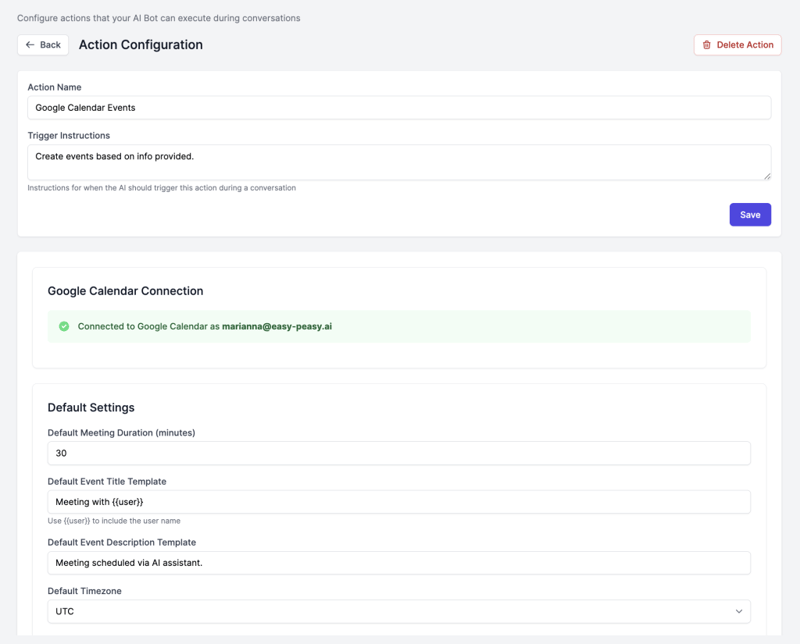
Configuration:
Name: Schedule Demo Call
Description: Book product demo calls with prospects
Trigger Condition: When user wants to schedule a demo, meeting, or consultation
Calendar ID: [email protected]
Default Duration: 30 minutes
Timezone: UTC
Features:
Check Availability
- Bot checks calendar for open slots
- Suggests available times to user
- Respects working hours and holidays
Send Invitations
- Automatic calendar invites to attendees
- Includes video meeting link (Google Meet)
- Sets up email reminders
- Add to attendee’s calendar with one click
Use Cases:
1. Sales Demos
- User: “I’d like to see a demo of your product”
- Bot: “Great! I have availability this week. Which day works best for you: Wednesday at 2 PM, Thursday at 10 AM, or Friday at 3 PM?”
- User: “Thursday at 10 works”
- Bot: [Creates calendar event] “Perfect! You’re all set for Thursday, January 18th at 10:00 AM EST. I’ve sent a calendar invite to your email with a Google Meet link.”
2. Customer Support
- Schedule technical support calls
- Book onboarding sessions
- Arrange troubleshooting meetings
3. Professional Services
- Consultation bookings (legal, financial, medical)
- Therapy or coaching sessions
- Training and workshops
4. Internal Operations
- Team meetings and standups
- Performance reviews
- Interview scheduling
5. Education
- Office hours with professors
- Tutoring sessions
- Parent-teacher conferences
Integration Flow:
1. User expresses interest in scheduling
↓
2. Bot checks Google Calendar availability
↓
3. Bot presents available time slots
↓
4. User selects preferred time
↓
5. Bot creates calendar event
↓
6. Calendar invitation sent to all attendees
↓
7. Bot confirms booking with details
↓
8. Automated reminders sent before event
Best Practices:
- ✅ Always set your timezone
Setting Up Your First Action
Let’s walk through setting up a complete action from scratch.
Example: E-commerce Product Lookup
Goal: Enable your bot to fetch real-time product information from your store’s API.
Step 1: Navigate to Actions
- Log into your Easy-Peasy.AI dashboard
- Select your bot
- Click on the “Actions” tab
- Click “Add Action”
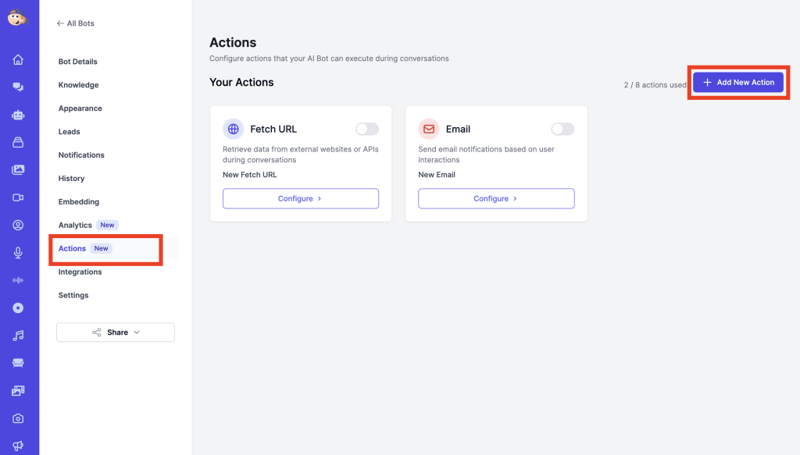
Step 2: Choose Action Type
- Select “Custom Action” from the list
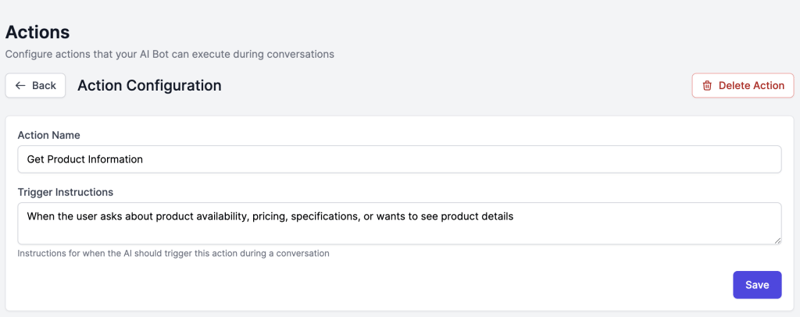
Step 3: Configure Basic Settings
Name: "Get Product Information"
Trigger Condition: "When the user asks about product availability, pricing, specifications, or wants to see product details"
💡 Tip: The trigger condition is crucial. Be specific about when the action should fire. Use natural language that describes user intent.
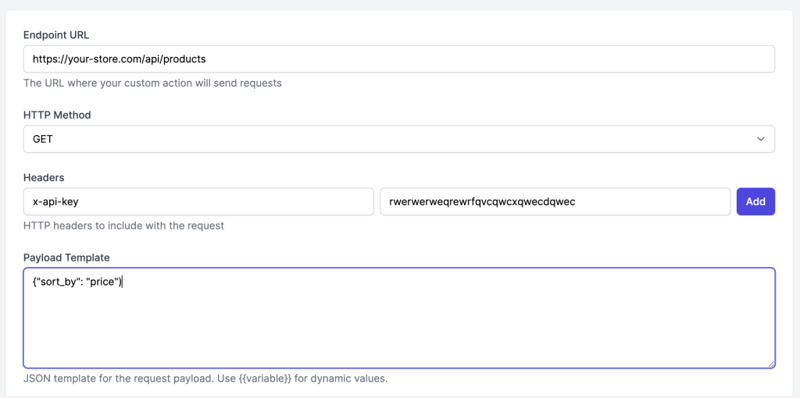
Step 4: Set Up API Connection
API Endpoint: https://your-store.com/api/products
Method: GET
Headers:
{
"Authorization": "Bearer YOUR_API_KEY",
"Content-Type": "application/json"
}
Query Parameters:
{
"product_name": "{{user_query}}",
"include": "price,availability,images"
}
Step 5: Test the Action
Click “Test Action” and enter a sample query:
Test Input: "Do you have blue hoodies?"
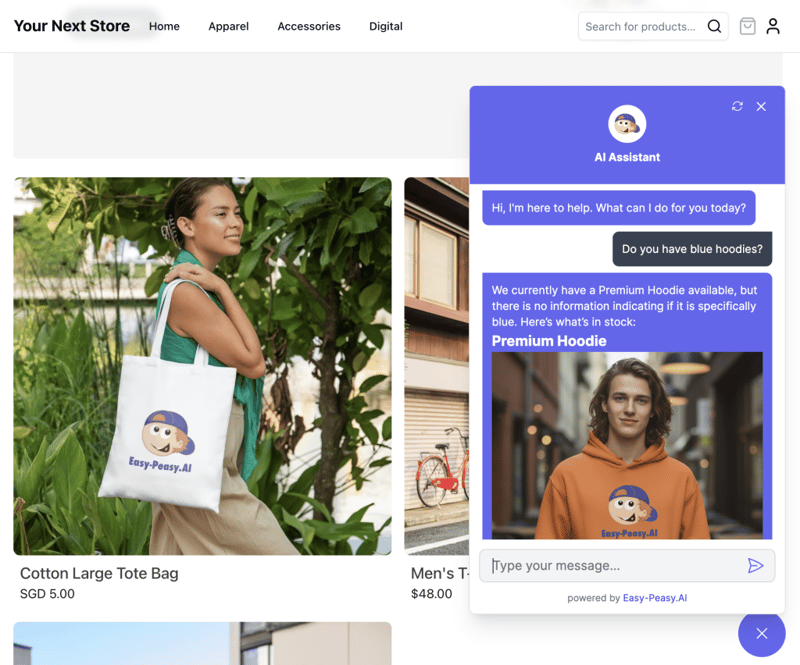
Step 6: Save and Deploy
- Click “Save Action”
- Toggle “Enable Action” to ON
- Test in the chat interface
- Monitor performance in Analytics and History
Best Practices for Bot Actions
Clear Trigger Conditions
❌ Bad:
"When user asks about products"
✅ Good:
"When user asks about product availability, stock levels, pricing, product specifications, or wants to see product images. Examples: 'Do you have hoodies?', 'How much are t-shirts?', 'Show me your products'"
Real-World Use Cases
Use Case 1: E-commerce Customer Support
Actions Used: Custom Action, Custom Form, Email Notification
Scenario: An online clothing store needs to handle customer inquiries 24/7.
Implementation:
- Product Inquiries: Custom Action fetches real-time inventory
- Bulk Orders: Custom Form collects business customer information
- Order Issues: Email Notification escalates to support team
Results:
- 70% of customer inquiries resolved without human intervention
- Average response time: <30 seconds (vs. 4 hours with email)
- 300% increase in bulk order requests captured
Use Case 2: SaaS Company Lead Generation
Actions Used: Custom Button, Custom Form, Google Calendar, Email Notification
Scenario: B2B SaaS company wants to qualify leads and book demos automatically.
Flow:
- User: “I’m interested in your product”
- Bot: Shows Custom Buttons: “Book Demo” | “Pricing Info” | “Technical Docs”
- User clicks “Book Demo”
- Bot: Presents Custom Form for qualification (company size, use case, role)
- Bot: Checks Google Calendar and offers available time slots
- User selects time
- Bot: Creates calendar event, sends Email Notification to sales team
- Sales rep joins pre-qualified demo call
Results:
- 85% of demos are pre-qualified (vs. 40% with manual booking)
- Sales team saves 15 hours/week on scheduling
- Demo show-up rate increased from 60% to 82%
Use Case 3: Financial Advisory Firm
Actions Used: Code Interpreter, Custom Form, Email Notification, Google Calendar
Scenario: Financial advisors need to provide quick calculations and book consultations.
Examples:
Retirement Calculator:
- User: “How much do I need to save for retirement?”
- Bot: Presents Custom Form (current age, retirement age, desired income, current savings)
- Bot: Uses Code Interpreter to calculate:
- Required monthly savings
- Total nest egg needed
- Investment return assumptions
- Generates projection graph
- Bot: “Based on your goals, you’ll need to save $1,847/month. Would you like to schedule a consultation to discuss strategies?” (Google Calendar)
Results:
- 40% increase in consultation bookings
- Clients arrive to meetings better informed
- Advisors focus on complex planning vs. basic calculations
Use Case 4: Healthcare Appointment Booking
Actions Used: Google Calendar, Custom Form, Email Notification, Fetch URL
Scenario: Medical clinic automates appointment scheduling and patient intake.
Flow:
- User: “I need to see a doctor for back pain”
- Bot: Checks Google Calendar for doctor availability
- Bot: “Dr. Smith has openings this week: Tuesday 2 PM, Wednesday 10 AM, Friday 4 PM”
- User: “Tuesday at 2 PM”
- Bot: Presents Custom Form for patient intake (insurance, symptoms, medical history)
- Bot: Creates Google Calendar event
- Bot: Sends Email Notification to clinic staff
- Bot: Uses Fetch URL to check insurance verification API
- Bot: Confirms appointment with insurance coverage details
Results:
- 90% of appointments booked outside business hours
- Front desk staff reduced by 2 FTE
- Patient wait time for appointment decreased from 7 days to 3 days
- HIPAA-compliant handling of sensitive data
Use Case 5: Real Estate Agency
Actions Used: Web Search, Custom Action, Custom Form, Email Notification, Custom Button
Scenario: Real estate agency helps buyers find properties and schedule viewings.
Flow:
- User: “I’m looking for a 3-bedroom house in Austin under $500k”
- Bot: Custom Action queries MLS database
- Bot: Returns matching properties with images
- User: “Tell me about the neighborhood safety”
- Bot: Web Search for crime statistics and school ratings
- Bot: Custom Buttons: “Schedule Viewing” | “Get Mortgage Quote” | “See More Photos”
- User clicks “Schedule Viewing”
- Bot: Custom Form collects contact info and preferred times
- Bot: Email Notification to agent
- Agent confirms viewing time via bot
Results:
- Lead response time: 5 minutes (vs. 4 hours)
- 3x more property viewings scheduled
- Agents focus on serious buyers (pre-qualified)
- 25% increase in closed deals
Combining Multiple Actions
The real power of Bot Actions comes from using them together in intelligent workflows.
Pattern 1: Research → Form → Notification
Use Case: Conference Registration
1. User: "I want to register for the AI Summit"
2. Web Search: Find conference dates, location, pricing
3. Custom Button: "Register Now" | "View Agenda" | "Hotel Info"
4. Custom Form: Collect registration details
5. Custom Action: Process payment via Stripe API
6. Email Notification: Send confirmation to attendee + organizers
7. Google Calendar: Add conference dates to calendar
Pattern 2: Query → Calculate → Action
Use Case: Loan Application
1. User: "Can I afford a $300k house?"
2. Custom Form: Collect income, down payment, credit score
3. Code Interpreter: Calculate:
- Maximum loan amount
- Monthly payment
- Required down payment
- Debt-to-income ratio
4. Custom Action: Check pre-approval status via bank API
5. Custom Button: "Apply Now" | "Adjust Parameters" | "Talk to Advisor"
6. Google Calendar: Schedule consultation if needed
Pattern 3: Fetch → Compare → Recommend
Use Case: Product Comparison
1. User: "Which laptop should I buy for video editing?"
2. Custom Form: Budget, preferred brands, must-have features
3. Custom Action: Query product database
4. Fetch URL: Scrape competitor prices
5. Web Search: Find expert reviews and benchmarks
6. Code Interpreter: Calculate value scores
7. Custom Button: Show top 3 recommendations with "Buy Now" links
8. Email Notification: Send comparison report to user
Pattern 4: Monitor → Alert → Escalate
Use Case: Critical System Monitoring
1. Custom Action: Continuously monitor API health
2. If error rate > 5%:
- Email Notification: Alert engineering team
- Custom Button: "View Dashboard" | "Run Diagnostics" | "Contact On-Call"
3. Code Interpreter: Analyze error logs
4. If critical:
- Email Notification: Escalate to CTO
- Google Calendar: Create emergency response meeting
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Issue 1: Action Not Triggering
Symptoms: Bot doesn’t use action when expected
Possible Causes:
- Trigger condition is too narrow or specific
- Action is disabled
- Conflicting actions with similar triggers
Solutions: ✅ Broaden trigger condition with more examples ✅ Check action is enabled in dashboard ✅ Test with exact phrasing that should trigger
Issue 3: Form Not Submitting
Symptoms: User fills form but nothing happens
Possible Causes:
- Required fields not filled
- Validation failing
- Form submit action not configured
- Network error during submission
Solutions: ✅ Clearly mark required fields ✅
Issue 4: Slow Response Times
Symptoms: Bot takes long time to respond after action
Possible Causes:
- Slow external API
- Multiple sequential API calls
- Large data processing
- No caching implemented
Solutions: ✅ Implement caching for frequently accessed data ✅ Use asynchronous/parallel API calls when possible ✅ Add loading indicators ✅ Optimize API queries (limit fields, use pagination) ✅ Use faster endpoints or CDNs ✅ Consider webhook-based approach for long-running tasks
Issue 5: Calendar Double-Booking
Symptoms: Same time slot booked multiple times
Possible Causes:
- Race condition (multiple users booking simultaneously)
- Calendar not refreshing availability
- Buffer time not configured
- Multiple calendars not synced
Solutions: ✅ Implement pessimistic locking (reserve slot temporarily) ✅ Refresh calendar before confirming booking ✅ Set appropriate buffer time between meetings ✅ Sync all team member calendars ✅ Show “Booking in progress…” to prevent double-clicks
Issue 6: Email Not Delivered
Symptoms: Email notification not received
Possible Causes:
- Email in spam folder
- Incorrect email address
- SPF/DKIM not configured
- Email service rate limits
- Email template has errors
Solutions: ✅ Set up SPF, DKIM, DMARC records ✅ Validate email addresses before sending ✅ Use reputable email service (SendGrid, AWS SES) ✅ Test email templates thoroughly ✅ Monitor email delivery rates ✅ Provide alternative notification methods (SMS, in-app)
Email Deliverability Checklist:
- [ ] SPF record configured
- [ ] DKIM signing enabled
- [ ] DMARC policy set
- [ ] Sender reputation good
- [ ] No blacklisted IPs
- [ ] Valid unsubscribe link
- [ ] Email template mobile-responsive
- [ ] No spam trigger words
Frequently Asked Questions
General Questions
Q: How many actions can I add to one bot?
A: You can add unlimited actions to a bot. However, some action types are “singletons” (Web Search, Code Interpreter, Fetch URL, Google Calendar) meaning you can only have one of each type per bot. This is because these actions are automatically invoked when needed rather than based on specific triggers.
Q: Do actions work with all AI models?
A: Yes, actions work with all supported AI models (GPT, Claude, Gemini, Llama, etc.). However, models with stronger reasoning capabilities (like GPT-5, Claude Opus, Gemini Pro) tend to be better at determining when to use actions.
Q: Can I use actions with the free plan?
A: Yes, one action is allowed.
Technical Questions
Q: What happens if an external API is down?
A: The bot will return the error message you configured, or a default fallback response.
Q: How long can a Code Interpreter script run?
A: Maximum 60 seconds execution time with 512MB RAM.
Q: Can I modify actions after deployment?
A: Yes, you can edit actions anytime. Changes take effect immediately. We recommend testing in a separate bot before modifying production bots.
Security & Privacy
Q: Where are API keys stored?
A: API keys are encrypted at rest using AES-256 and never exposed in client-side code or logs.
Q: Is code executed in Code Interpreter sandboxed?
A: Yes, code runs in isolated Docker containers with no network access to internal systems, limited memory, and no persistent storage.
Q: How is user data from forms stored?
A: Form submissions are stored in our secure database and are accessible only to authorized users in your account. You can export or delete data anytime. We’re GDPR , ISO27001 and SOC2 compliant.
Integration Questions
Q: Can I integrate with Salesforce/HubSpot/custom CRM?
A: Yes, use Custom Actions to call your CRM’s API. We also have native integrations with popular CRMs. Check our Integrations page for details.
Q: Does it work with Microsoft Outlook Calendar?
A: Currently only Google Calendar is natively supported. For Outlook, use Zapier integration or our API to build custom integration.
Q: Can I trigger Zapier workflows from bot actions?
A: Yes! Use Custom Actions to call Zapier webhooks, enabling integration with 5,000+ apps.
Conclusion
Bot Actions represent the future of conversational AI – chatbots that don’t just chat, but actually DO things. By combining knowledge bases with actions, you create truly intelligent agents that can:
✅ Access real-time information
✅ Complete complex tasks
✅ Integrate with your existing systems
✅ Provide personalized experiences
✅ Automate entire workflows
The possibilities are limitless. Whether you’re building a customer support bot, a sales assistant, an internal tool, or something entirely new – Actions give your bot superpowers.
Ready to build your agentic chatbot?
Questions? Feedback? Contact us
About Easy-Peasy.AI
Easy-Peasy.AI is an all-in-one AI platform that helps businesses build intelligent chatbots, automate workflows, and create content – all without code. We’re on a mission to make advanced AI accessible to everyone.