Bacterial Cell Division: Understanding FtsZ Protein Process
Prompt
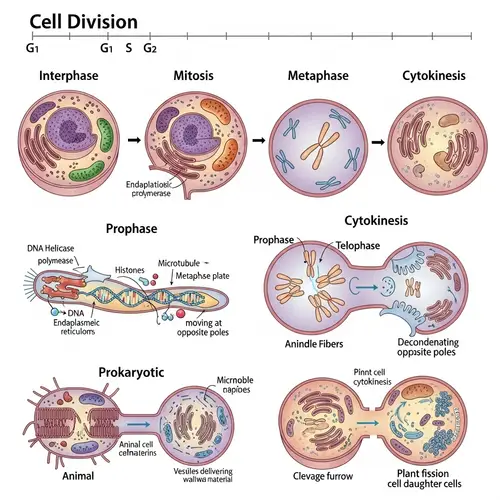
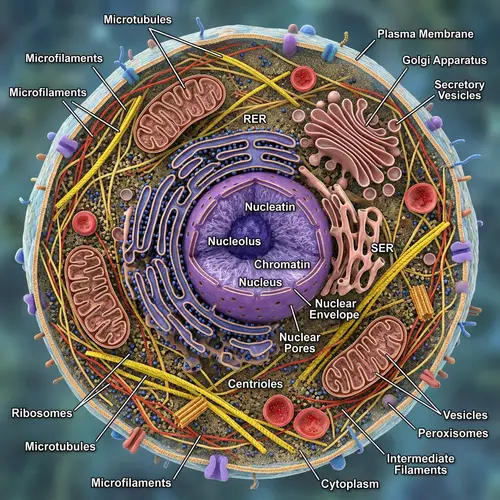
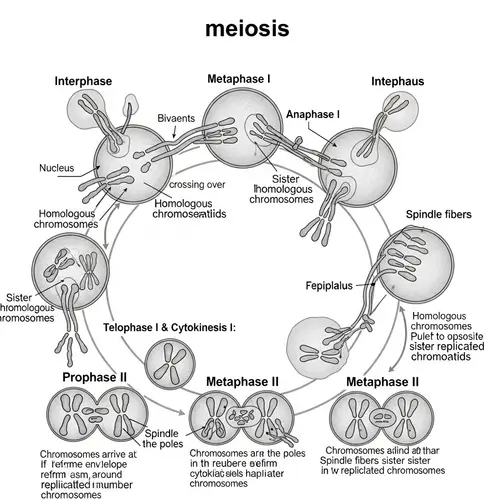
Please generate an image illustrating the process of bacterial cell division involving FtsZ protein. Start by showing a bacterial cell replicating its DNA, then show two identical DNA molecules each attached to the cell membrane. Next, depict the division site often located on the DNA region. In the future division site, show the formation of a macromolecular complex called 'divisome', mediating distinct steps during cell division. Illustrate FtsZ polymerizing at the division site into a ring-shaped structure, the Z-ring, which serves as a scaffold for recruiting other division proteins and constricting the cell. Also, present other proteins such as FtsA and ZipA anchoring the Z-ring to the inner cell membrane and FtsK involved in segregating the duplicated DNA. Display FtsI/PBP3, a penicillin-binding protein, building up the peptidoglycan layer specifically at the septum site, forming the peptidoglycan cell wall. As this layer is formed, show the Z-ring contracting and the cell membrane pinching inward, gradually forming a wall-like structure called septum. Progressively illustrate septum separating into two new cells. Lastly, depict a close-up of the three-dimensional structure of FtsZ showing the N-terminal domain with six β-sheets surrounded by α-helices, the C-terminal domain with four parallel arranged β-sheets surrounded by α-helices, the inter-domain cleft, the GTP binding site, and the polymerization interface.
More images like this

Create Your Own AI Images
Generate stunning AI images with our easy-to-use image generator
Supported Styles
Our AI image generator supports 20+ styles and all diverse styles - just select the appropriate style and enter text in your language of choice.
Valentine's Day Photo
Valentine's Day Card
Oil Painting
Realistic Photo
Cyberpunk
Watercolor
Pencil drawing
Cartoon
Disney
Pixar
Disney Poster
Movie Poster
Anime
Mosaic
3D Model
Portrait
Icon
Sticker
Landscape
Pokemon
Logo
Business Card
Band Logo
Furry
T-Shirt Design
Jersey
Hoodie
Tattoo
Birth Flower Tattoo
Fantasy
Fantasy Map
DND
Album Cover
Pixel Art
Coloring Page
Coloring Book
Texture
Animal
Car
Lego
Minecraft
Hello Kitty
Mascot
Superhero
Monster
Sewing Pattern
Crochet Pattern
Clothing Design
Architecture
Character
Baby
Book Cover
Book Illustration
Outfit
YouTube Thumbnail
Banner
Sprite Sheet
Caricature
Scene
Mugshot
Face
Human
Food
Yearbook Photo
Graduation Photo
Vintage Photo
Christmas Photo
Christmas Card
Muppet
Cake
Costume
Cat
Dog
Jewelry
LinkedIn Profile Picture
Graffiti
Product Design
Bible Art
Sketch
House
Home Exterior Design
Landscape Design
Fusion
Doodle
Stadium
Patch
Planet
Silhouette
Postcard
Family Crest
Stained Glass
Van Gogh
Warhol
Picasso
Leonardo da Vinci
Claude Monet
Salvador Dali
Jackson Pollock
Mark Rothko
Kandinsky
Gustav Klimt
Hokusai
Vector (SVG)
Cyborg
Synthwave
Neonpunk
Analog
Product Photography
Celebrity
Line Art
Avatar
Background Art
Concept Art
Photo Restoration
Game Assets
Fashion Design
NFT Art
Packaging Design
Comic Creation
Pattern Art
Character Design
Restaurant Menu Design
Podcast Cover
Instagram Post
Luxury Lifestyle
Selfie
Dating Profile
Glamour
Old Money
Speaker
Fitness
Muscle
Mythical Creature
Villain
Ghibli
Isometric Art
Chalk Art
Holographic
Art Nouveau
Collage Art
Steampunk
Claymation
Glitch Art
Gothic
Furniture
Uniform
Pet Portrait
Nail Art
Horror Art
Pop Art
Typography Art
Action Figure
Fight
Wedding Photo
Age Progression
Tarot Card
Magazine Cover
Dragon
Political Cartoon
Therapist Headshots
Lawyer Headshots
Comedian Headshots
Teacher Headshots
Life Coach Headshots
Doctor Headshots
Real Estate Agent Headshots
Model Headshots
Corporate Headshots For Your Team
Author Headshots
Dating Headshots
CEO Headshots
Actor Headshots
Professional Headshots
LinkedIn Headshots
Dancer Headshots
Outdoor Headshots
Personal Trainer Headshots
Chef Headshots
Nurse Headshots
Hair Stylist Headshots
Musician Headshots
Interior Designer Headshots
Insurance Agent Headshots
Dentist Headshots
Financial Advisor Headshots
Infographic
Poster
Invitation
Flyer
Moodboard
Instagram Photos
Halloween Photos
Fitness Influencer
Polaroid Photos
Tinder
Hinge
Yoga & Wellness
Entrepreneur
Bumble
Beach Bikini
Girlfriend
Chinese New Year
Hanukkah
Hair Color Try On
Weight Loss Simulator
ASCII Art
Wallpaper
Emoji
Meme
Floor Plan
Map
Hairstyle
Room Design
Manga
Blueprint
Wireframe
Makeup
Passport Photo
ID Photo
Couple Photo
Certificate
Chibi
Calligraphy
Abstract Art
Profile Picture
Photo Booth
Garden Design
Shoe Design
Trophy
Mandala
Easter Photo
Thanksgiving Photo
Eid Photo
Diwali Photo
Ramadan Photo
4th of July Photo
Birthday Photo
Birthday Card
Baby Shower Photo
Back to School Photo
Engagement Photo
Newborn Photo
Prom Photo
Aesthetic Photo
Retro Photo
Surreal Art
Psychedelic Art
Minimalist Art
Geometric Art
Kawaii
Pastel Art
Sports Photo
Military Photo
School Photo
Create Faster With AI.
Try it Risk-Free.
Stop wasting time and start creating high-quality content immediately with power of generative AI.